EMPAVELI safety data in clinical and real-world settings
EMPAVELI safety
Adverse reactions reported at Week 16 in ≥5% of patients treated with EMPAVELI1
*Grouped terms.
†Term includes injection-site erythema, injection-site reaction, injection-site swelling, injection-site induration, injection-site bruising, injection-site pain, injection-site pruritus, vaccination site reaction, administration site swelling, injection-site hemorrhage, injection-site edema, injection-site warmth, administration site pain, application site pain, injection-site mass, injection-site rash, vaccination site pain.1
Serious adverse reactions through Week 16 were reported in 17% of patients receiving EMPAVELI1
- The most common serious adverse reaction in patients was infections (5%)1
- During the PEGASUS 16-week pivotal trial, no patients in either the EMPAVELI or eculizumab group had an event of thrombosis3
- During the 32-week OLP, serious adverse reactions were reported in 18 patients (23%)1
- Additional adverse reactions reported in >5% of patients treated with EMPAVELI during the OLP compared to the RCP were cough (12%), arthralgia (8%), oropharyngeal pain (8%), pyrexia (8%), pain in extremity (7%), thrombocytopenia (7%), abdominal distension (5%), acute kidney injury (5%), anxiety (5%), and myalgia (5%)1
- In the PEGASUS trial, 2 patients taking EMPAVELI had side effects related to thrombosis. They were not deemed related to EMPAVELI4
EMPAVELI safety
Adverse reactions reported at Week 26 in ≥5% of patients treated with EMPAVELI1
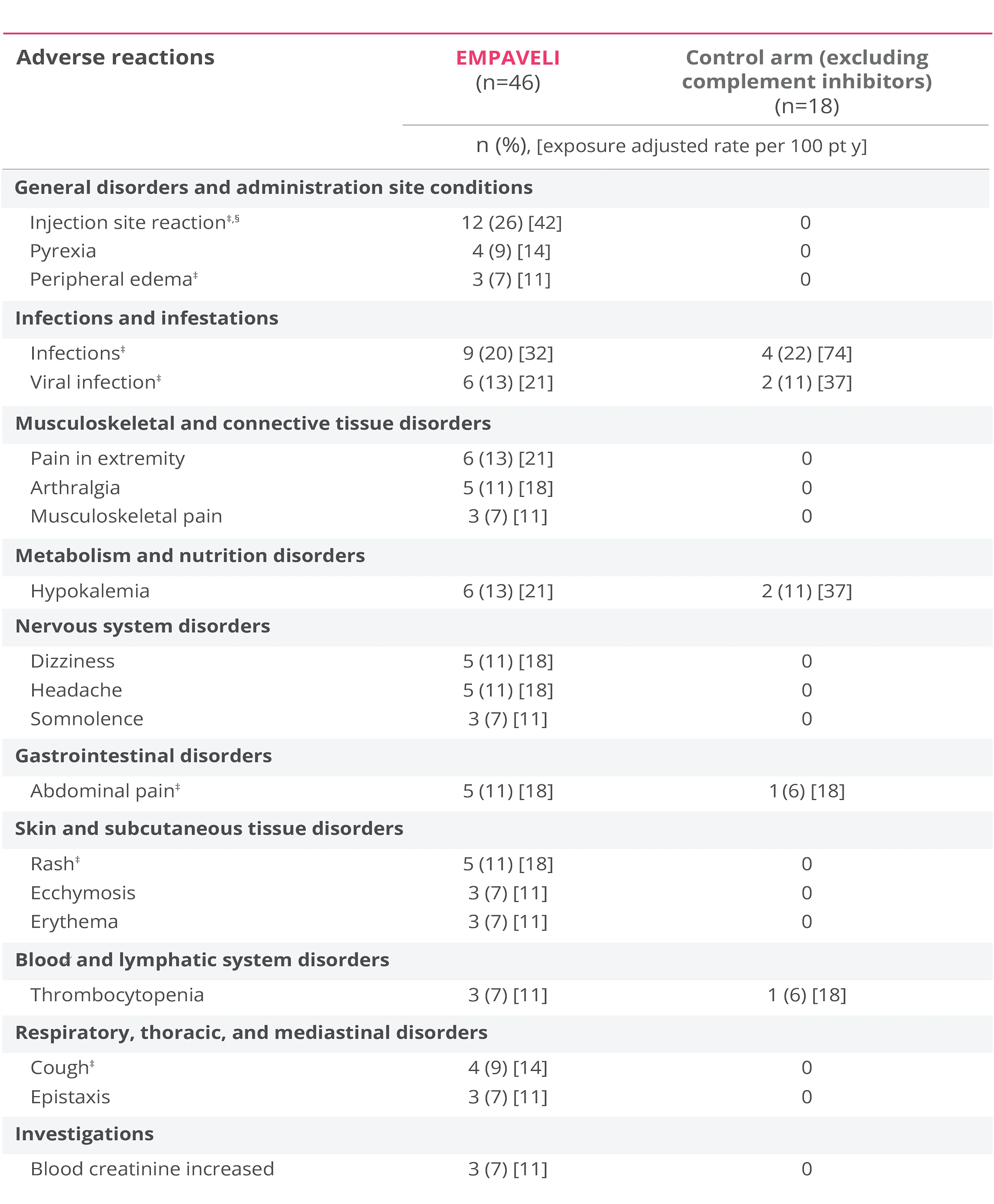
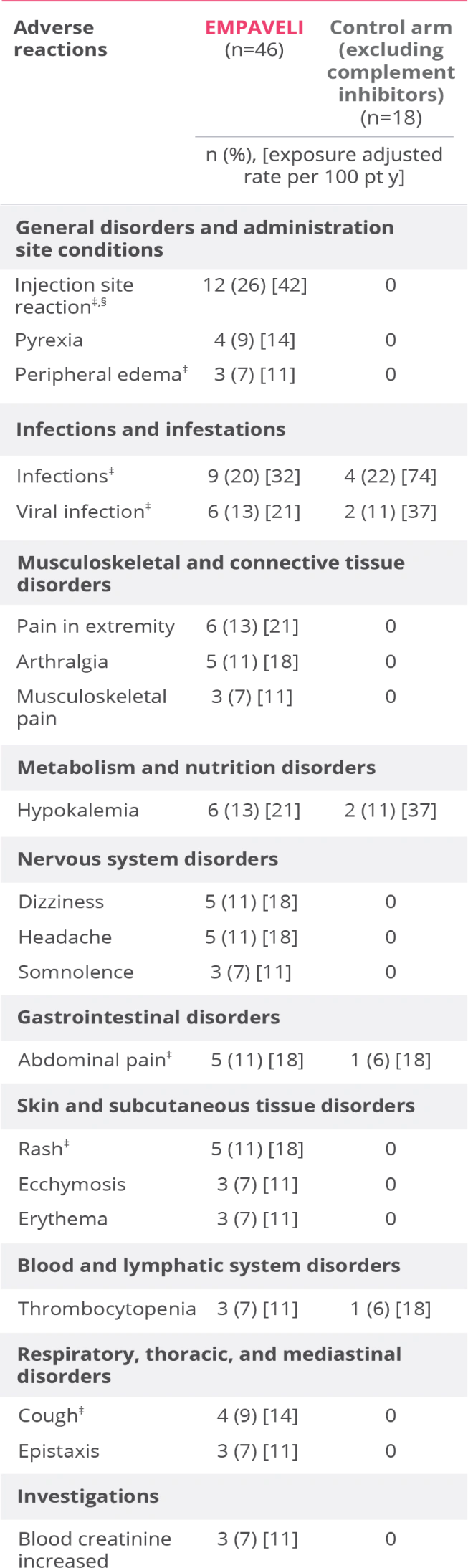
EMPAVELI (n=46) group includes patients who received EMPAVELI at any point during the study, including patients randomized to EMPAVELI (n=35) and patients randomized to the control arm and crossed over to EMPAVELI treatment (n=11).1
‡Grouped terms.
§Term includes injection-site bruising, injection-site hemorrhage, injection-site swelling, application site reaction, infusion-site pruritus, injection-site erythema, injection-site rash, puncture site reaction.1
Serious adverse reactions through Week 26 were reported in 13% of patients receiving EMPAVELI1
- The most common adverse reactions (≥10%) in patients were injection site reactions, infections, viral infection, pain in extremity, hypokalemia, arthralgia, dizziness, abdominal pain, rash, headache1
- During the PRINCE 26-week clinical trial, there were no reported thrombosis events4
- Three patients (2 in the EMPAVELI group and 1 in the control group) discontinued the study, none due to an adverse reaction1
Clinical and real-world meningococcal and thrombosis rates¶
- As of 08/13/2025, worldwide, no cases of encapsulated meningococcal infection in any adult PNH patient treated with pegcetacoplan have been identified3
- Worldwide, clinical trial and postmarketing settings comprise a cumulative systemic exposure of3:
- 174 patients with ≥590 patient-years and
- 1496 patients with ≥1800 patient-years in the PNH population, respectively
- Patients were vaccinated according to Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) guidelines prior to treatment with pegcetacoplan1
- As of 08/13/2025, the thrombosis rate in the PNH population was 0.565 events per 100 patient-years3
¶As of 08/13/2025. Includes patients in clinical trials and on commercial drug.3
In a combination of C5i (eculizumab)-experienced and complement inhibitor-naïve patients3
Long-term integrated safety analysis up to 3 years3,4,6
- The most common AEs (≥10%)# were nasopharyngitis (16.7%), upper respiratory tract infection (14.4%), urinary tract infection (12.9%), injection site reactions (36.4%), abdominal pain (18.2%), fatigue (18.2%), headache (16.7%), and cough (12.1%)—consistent with those reported in the original studies3,6,7
- Two serious AEs deemed related to EMPAVELI occurred3
- 1 case of biliary sepsis in PEGASUS
- 1 case of sepsis in PRINCE
- One patient taking EMPAVELI had side effects related to thrombosis during the long-term integrated analysis. They were deemed not related to EMPAVELI4
- No new safety findings were identified4
#COVID-19 was excluded due to the pandemic and underlying immunocompromised population of PNH.
AE=adverse events; C5i=C5 inhibitor; OLP=open-label period; PNH=paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria; RCP=randomized control period.
References: 1. EMPAVELI [prescribing information]. Waltham, MA: Apellis Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; 2025. 2. Heo YA. Pegcetacoplan: a review in paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria. Drugs. 2022;82(18):1727-1735. doi:10.1007/s40265-022-01809-w 3. Data on file. Apellis Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Waltham, MA. 4. de Castro C, Kelly RJ, Griffin M, et al. Efficacy and safety maintained up to 3 years in adults with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria receiving pegcetacoplan. Adv Ther. 2025;42(9):4641-4658. 5. Wong RSM, Navarro-Cabrera JR, Comia NS, et al. Pegcetacoplan controls hemolysis in complement inhibitor-naive patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood Adv. 2023;7(11):2468-2478. doi:10.1182/bloodadvances.2022009129 6. Horneff R, Czech B, Yeh M, Surova E. Three years on: the role of pegcetacoplan in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) since its initial approval. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(16):8698. doi:10.3390/ijms25168698 7. de Castro C, Mulherin B, Patriquin CJ, et al. Efficacy and safety is maintained up to 3 years in adults with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria receiving pegcetacoplan. Blood. 2023;142(suppl1):574-576.


