IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
WARNING: SERIOUS INFECTIONS CAUSED BY ENCAPSULATED BACTERIA
EMPAVELI, a complement inhibitor, increases the risk of serious infections, especially those caused by encapsulated bacteria, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae, Neisseria meningitidis, and Haemophilus influenzae type B. Life-threatening and fatal infections with encapsulated bacteria have occurred in patients treated with complement inhibitors. These infections may become rapidly life-threatening or fatal if not recognized and treated early.
- Complete or update vaccination for encapsulated bacteria at least 2 weeks prior to the first dose of EMPAVELI, unless the risks of delaying therapy with EMPAVELI outweigh the risks of developing a serious infection. Comply with the most current Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommendations for vaccinations against encapsulated bacteria in patients receiving a complement inhibitor.
- Patients receiving EMPAVELI are at increased risk for invasive disease caused by encapsulated bacteria, even if they develop antibodies following vaccination. Monitor patients for early signs and symptoms of serious infections and evaluate immediately if infection is suspected.
Because of the risk of serious infections caused by encapsulated bacteria, EMPAVELI is available only through a restricted program under a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) called the EMPAVELI REMS.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Hypersensitivity to pegcetacoplan or to any of the excipients
- For initiation in patients with unresolved serious infection caused by encapsulated bacteria including Streptococcus pneumoniae, Neisseria meningitidis, and Haemophilus influenzae type B
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Serious Infections Caused by Encapsulated Bacteria
EMPAVELI, a complement inhibitor, increases a patient’s susceptibility to serious, life-threatening, or fatal infections caused by encapsulated bacteria including Streptococcus pneumoniae, Neisseria meningitidis (caused by any serogroup, including non-groupable strains), and Haemophilus influenzae type B. Life-threatening and fatal infections with encapsulated bacteria have occurred in both vaccinated and unvaccinated patients treated with complement inhibitors. The initiation of EMPAVELI treatment is contraindicated in patients with unresolved serious infection caused by encapsulated bacteria.
Complete or update vaccination against encapsulated bacteria at least 2 weeks prior to administration of the first dose of EMPAVELI, according to the most current ACIP recommendations for patients receiving a complement inhibitor. Revaccinate patients in accordance with ACIP recommendations considering the duration of therapy with EMPAVELI. Note that, ACIP recommends an administration schedule in patients receiving complement inhibitors that differs from the administration schedule in the vaccine prescribing information. If urgent EMPAVELI therapy is indicated in a patient who is not up to date with vaccines against encapsulated bacteria according to ACIP recommendations, provide the patient with antibacterial drug prophylaxis and administer these vaccines as soon as possible. The benefits and risks of treatment with EMPAVELI, as well as the benefits and risks of antibacterial drug prophylaxis in unvaccinated or vaccinated patients, must be considered against the known risks for serious infections caused by encapsulated bacteria.
Vaccination does not eliminate the risk of serious encapsulated bacterial infections, despite development of antibodies following vaccination. Closely monitor patients for early signs and symptoms of serious infection and evaluate patients immediately if an infection is suspected. Inform patients of these signs and symptoms and instruct patients to seek immediate medical care if these signs and symptoms occur. Promptly treat known infections. Serious infection may become rapidly life-threatening or fatal if not recognized and treated early. Consider interruption of EMPAVELI in patients who are undergoing treatment for serious infections.
EMPAVELI is available only through a restricted program under a REMS.
EMPAVELI REMS
EMPAVELI is available only through a restricted program under a REMS called EMPAVELI REMS, because of the risk of serious infections caused by encapsulated bacteria. Notable requirements of the EMPAVELI REMS include the following:
Under the EMPAVELI REMS, prescribers must enroll in the program. Prescribers must counsel patients about the risks, signs, and symptoms of serious infections caused by encapsulated bacteria, provide patients with the REMS educational materials, ensure patients are vaccinated against encapsulated bacteria at least 2 weeks prior to the first dose of EMPAVELI, prescribe antibacterial drug prophylaxis if patients’ vaccine status is not up to date and treatment must be started urgently, and provide instructions to always carry the Patient Safety Card both during treatment, as well as for 2 months following last dose of EMPAVELI. Pharmacies that dispense EMPAVELI must be certified in the EMPAVELI REMS and must verify prescribers are certified.
Further information is available at www.empavelirems.com or 1-888-343-7073.
Infusion-Related Reactions
Systemic hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., facial swelling, rash, urticaria) have occurred in patients treated with EMPAVELI, which may resolve after treatment with antihistamines. Cases of anaphylaxis leading to treatment discontinuation have been reported. If a severe hypersensitivity reaction (including anaphylaxis) occurs, discontinue EMPAVELI infusion immediately, institute appropriate treatment, per standard of care, and monitor until signs and symptoms are resolved.
Monitoring PNH Manifestations after Discontinuation of EMPAVELI
After discontinuing treatment with EMPAVELI, closely monitor for signs and symptoms of hemolysis, identified by elevated LDH levels along with sudden decrease in PNH clone size or hemoglobin, or reappearance of symptoms such as fatigue, hemoglobinuria, abdominal pain, dyspnea, major adverse vascular events (including thrombosis), dysphagia, or erectile dysfunction. Monitor any patient who discontinues EMPAVELI for at least 8 weeks to detect hemolysis and other reactions. If hemolysis, including elevated LDH, occurs after discontinuation of EMPAVELI, consider restarting treatment with EMPAVELI.
Interference with Laboratory Tests
There may be interference between silica reagents in coagulation panels and EMPAVELI that results in artificially prolonged activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT); therefore, avoid the use of silica reagents in coagulation panels.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
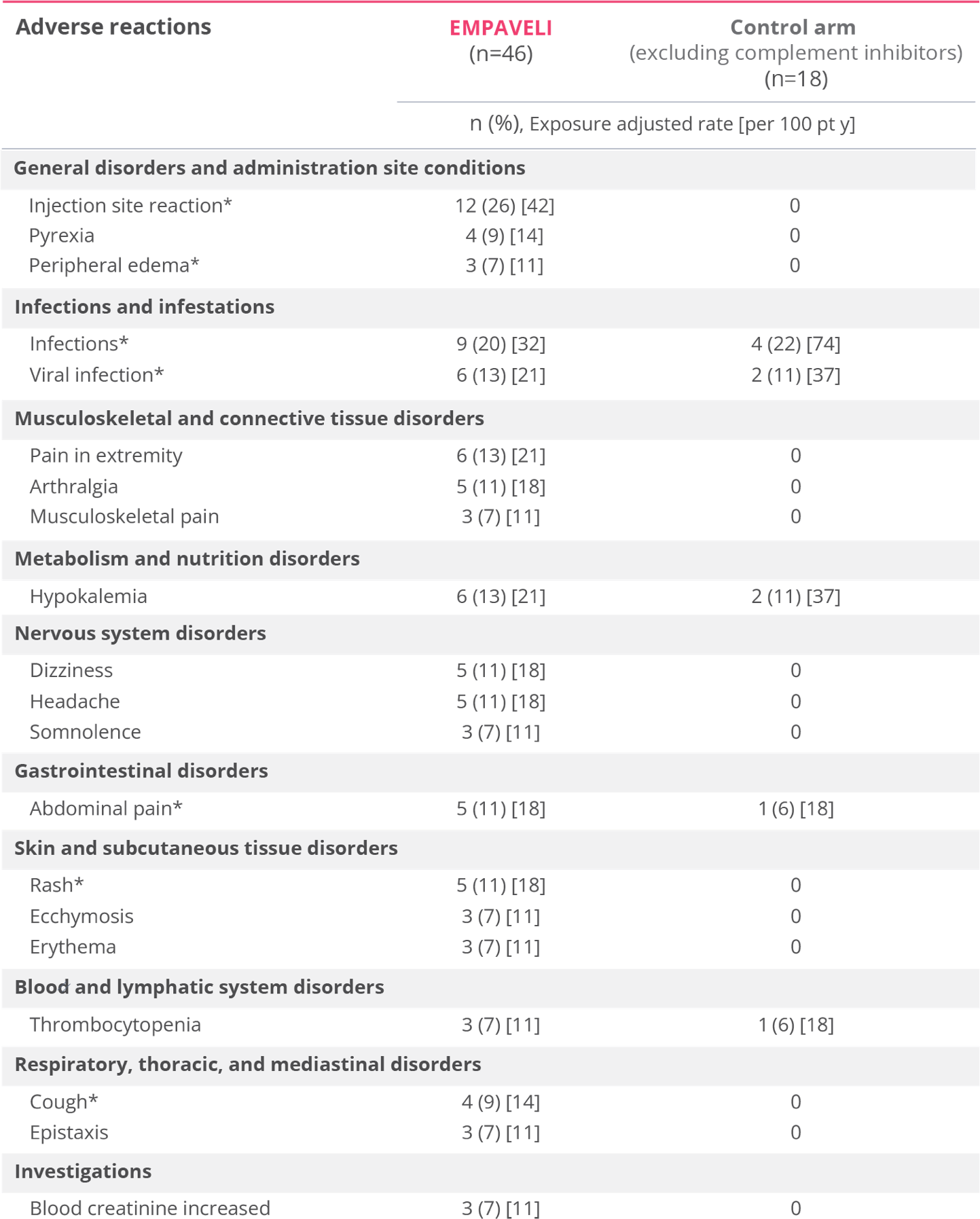
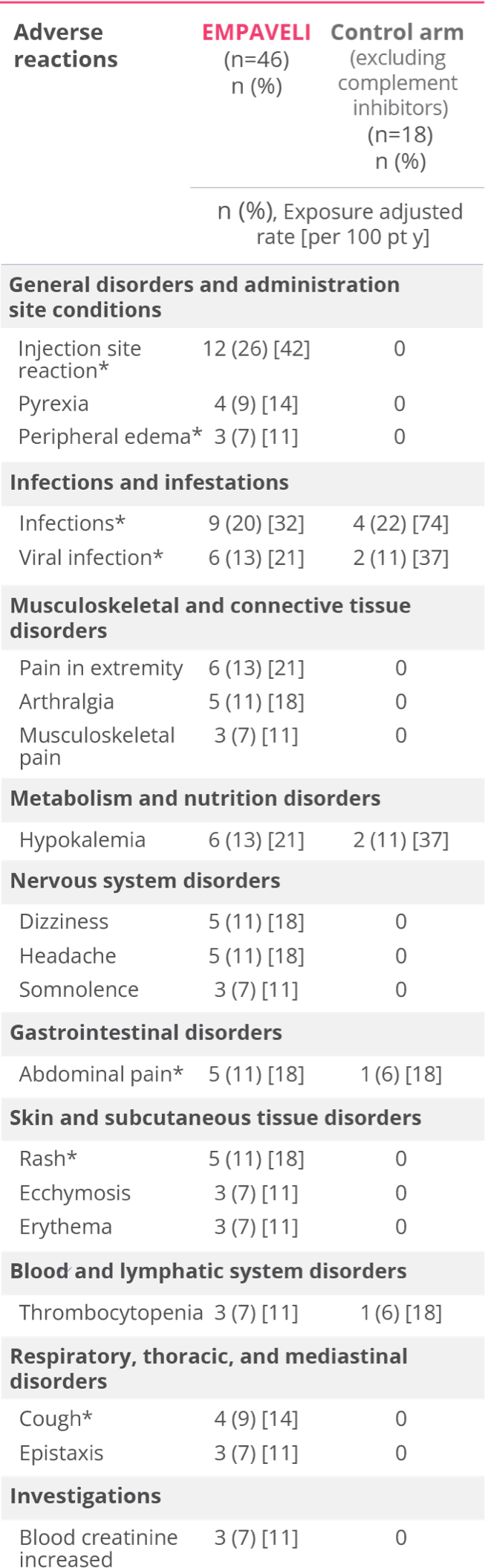
Most common adverse reactions in patients with PNH (incidence ≥10%) were injection‑site reactions, infections, diarrhea, abdominal pain, respiratory tract infection, pain in extremity, hypokalemia, fatigue, viral infection, cough, arthralgia, dizziness, headache, and rash.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Females of Reproductive Potential
EMPAVELI may cause embryo-fetal harm when administered to pregnant women. Pregnancy testing is recommended for females of reproductive potential prior to treatment with EMPAVELI. Advise female patients of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with EMPAVELI and for 40 days after the last dose.
INDICATION
EMPAVELI® (pegcetacoplan) is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH).
Please see full Prescribing Information, including Boxed WARNING regarding serious infections caused by encapsulated bacteria, and Medication Guide.